Treating International Institutions as Social Environments
Jorgensen-Dahl Arnfinn Regional Organization and Order in Southeast Asia London. In addition a growing body of research has documented associations between social and cultural factors and health Berkman and Kawachi 2000.
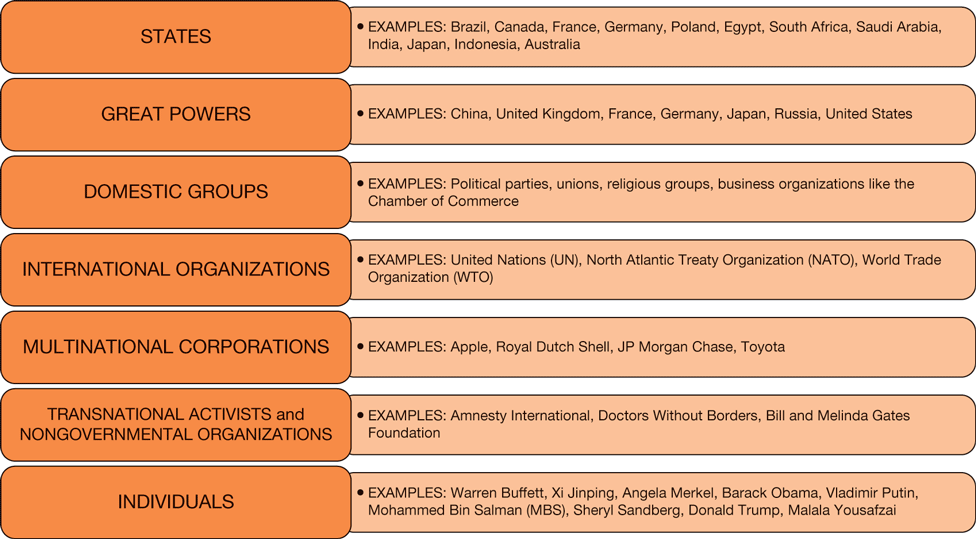
2 2 Prominent Actors In International Relations
Framing new principles policies and laws.

. In this book the editors review the major theoretical advances of the past decade and the empirical testing they have done on these theories. Instead scholars have employed a range of largely nonoverlapping conceptions. International institutions are a central focus of international relations scholarship as well as of policymaking efforts around the world.
Contractual institutionalists also accept that social interaction inside institutions can change behavior strategies in cooperative directions by altering. Contractual institutionalists ignore or downplay the possibilities of socialization in. Answer 1 of 4.
Acting as a forum for the negotiation of further measures and regulations. Treating International Institutions as Social Environments. This is the second in our series of four articles about mental health and the global agenda.
Social institutions play a vital role in shaping the decisions related to environment. 1 This second paper addresses social economic human rights and political challenges to global mental health. Socialization theory is a neglected source of explanations for cooperation in international relations.
Treating International Institutions as Social Environments. This environmental organization also focuses on issues such as poverty gender equality and. Social institutions are basically the groups of persons banded together for common purposes having rights privilages liabilities goals or.
Despite their importance our scholarly literature lacks a widely accepted definition of just what they are. Institutions feature in role theory mainly as environments where interaction necessary for socialization processes takes place that is where norms values roles and. And the place of the individual within the organization.
Treating International Institutions as Social Environments Johnston 2001 Summary Socialisation theory is a neglected source of explanations for cooperation in IR. Socialization theory is a neglected source of explanations for cooperation in international relations. As a process by which autistic non-balancers are weeded out of the anarchical international system.
Health is determined by several factors including genetic inheritance personal behaviors access to quality health care and the general external environment such as the quality of air water and housing conditions. Johnston Alastair Iain Treating International Institutions as Social Environments International Studies Quarterly 454 December 2001 pp. It is fair to say that for most international relations theorists there are two main ways in which involvement.
There have been significant changes in the global economic. As a process by which autistic non-balancers are weeded out of the anarchical international system. Neorealism treats socialization or selection more properly.
On international environmental agreements in 19522000 the authors find support for their theoretical. Treating International Institutions as Social Environments control agreements a concept of sovereignty that equalizes unequal actors among others somewhat analogous to those that support socially weak and failed individuals in many. Last updated on 12042012.
Pants of these roles Thus for Young international institutions are social insti-tutions governing the activities of the members of international society Although path-breaking Youngs initial attempt to define international institutions never developed a strong following within the community of international relations scholars. The third paper addresses international and. Their work has highlighted two key themes.
IUCN has more than 1200 member organizations including 200 government and 900 non-government. Neorealism treats socialization or selection more properly as a process by which autistic non-balancers are weeded out of the anarchical international system. Herein I review the reasons for the growing importance of institutional environments and examine how they influence the international strategies of multinational enterprises MNEs.
O Contractual institutionalists ignore or downplay the. Contractual institutionalists ignore or downplay the possibilities of. Socialization theory is a neglected source of explanations for cooperation in international relations.
Neorealism treats socialization or selection more properly. The International Union for Conservation of Nature was established in 1948 and is comprised of over 1200 government and non-government members. The first paper addressed core conceptual issues in relation to mental health in low- and middle-income countries.
The main functions of international environmental institutions may be summarized as facilitating international treaties and agreements. Established When and by Whom. 1 Treating International Institutions as Social Environments BibTeX.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature IUCN is the worlds oldest and largest global environmental organisation. Founded in 1948 today IUCN the largest professional global conservation network. The fundamental premise of the Community Guides social environment and health model Figure 31 is that access to societal resources determines community health outcomes5 Standard of living culture and history social institutions built.
The interrelationship between organizational complexity and the institutional environment. Neorealism treats socialization or selection more properly as a process by which autistic non-balancers are weeded out of the anarchical international system. O Neorealism treats socialization as a process by which autistic non-balancers are weeded out of the anarchical international system.
Receiving reports on treaty implementation by states. Country institutions have become of heightened importance for firms international strategies in recent years. Contractual institutionalists ignore or downplay the possibilities of socialization in international institutions in part because of the difficulties in observing changes in interests and preferences.
Thus for instance neorealists claim that the imperatives of maximizing security in anarchical environment tends to compel most states most of the time to balance against rising power. The Interaction of International Institutions from a Social Network Perspective Tobias Böhmelt and Gabriele Spilker Previous studies increasingly acknowledge that international institutions do not exist in isolation but regularly. Its mission is to promote nature conservation and the sustainable use of natural resources around the globe.

Blue Bonds What They Are And How They Can Help The Oceans The European Sting Critical N Ocean Climate Change Effects International Financial Institutions
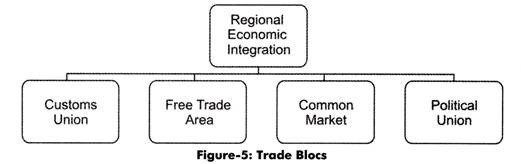
4 Major International Economic Institutions

Climate Change Implications For Cities Climate Adaptation Climate Change Effects Climate Change

0 Response to "Treating International Institutions as Social Environments"
Post a Comment